JSON Prompting is a technique for structuring instructions to AI models using the JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) format, making prompts clear, explicit, and machine-readable. Unlike traditional text-based prompts, which can leave room for ambiguity and misinterpretation, JSON prompts organize requirements as key-value pairs, arrays, and nested objects, turning vague requests into precise blueprints for the model to follow. This method greatly improves consistency and accuracy—especially for complex or repetitive tasks—by allowing users to specify things like task type, topic, audience, output format, and other parameters in an organized way that language models inherently understand. As AI systems increasingly rely on predictable, structured input for real-world workflows, JSON prompting has become a preferred strategy for generating sharper, more reliable results across major LLMs, including GPT-4, Claude, and Gemini.
In this tutorial, we’ll dive deep into the power of JSON prompting and why it can transform the way you interact with AI models.
We will walk you through the benefits of using JSON Prompting through coding examples —from simple text prompts to structured JSON prompts—and show you comparisons of their outputs. By the end, you’ll clearly see how structured prompts bring precision, consistency, and scalability to your workflows, whether you’re generating summaries, extracting data, or building advanced AI pipelines. Check out the FULL CODES here.


Installing the dependencies
import os
from getpass import getpass
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = getpass('Enter OpenAI API Key: ')To get an OpenAI API key, visit https://platform.openai.com/settings/organization/api-keys and generate a new key. If you’re a new user, you may need to add billing details and make a minimum payment of $5 to activate API access. Check out the FULL CODES here.
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()Structured Prompts Ensure Consistency
Using structured prompts, such as JSON-based formats, forces you to think in terms of fields and values — a true advantage when working with LLMs. Check out the FULL CODES here.
By defining a fixed structure, you eliminate ambiguity and guesswork, ensuring that every response follows a predictable pattern.
Here’s a simple example:
Summarize the following email and list the action items clearly.
Email:
Hi team, let's finalize the marketing plan by Tuesday. Alice, prepare the draft; Bob, handle the design.We’ll feed this prompt to the LLM in two ways and then compare the outputs generated by a free-form prompt versus a structured (JSON-based) prompt to observe the difference in clarity and consistency. Check out the FULL CODES here.
Free-Form Prompt
prompt_text = """
Summarize the following email and list the action items clearly.
Email:
Hi team, let's finalize the marketing plan by Tuesday. Alice, prepare the draft; Bob, handle the design.
"""
response_text = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-5",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt_text}]
)
text_output = response_text.choices[0].message.content
print(text_output)Summary:
The team needs to finalize the marketing plan by Tuesday. Alice will prepare the draft, and Bob will handle the design.
Action items:
- Alice: Prepare the draft of the marketing plan by Tuesday.
- Bob: Handle the design by Tuesday.
- Team: Finalize the marketing plan by Tuesday.JSON Prompt
prompt_json = """
Summarize the following email and return the output strictly in JSON format:
{
"summary": "short summary of the email",
"action_items": ["task 1", "task 2", "task 3"],
"priority": "low | medium | high"
}
Email:
Hi team, let's finalize the marketing plan by Tuesday. Alice, prepare the draft; Bob, handle the design.
"""
response_json = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-5",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a precise assistant that always replies in valid JSON."},
{"role": "user", "content": prompt_json}
]
)
json_output = response_json.choices[0].message.content
print(json_output)
{
"summary": "Finalize the marketing plan by Tuesday; Alice to draft and Bob to handle design.",
"action_items": [
"Alice: prepare the draft",
"Bob: handle the design",
"Team: finalize the marketing plan by Tuesday"
],
"priority": "medium"
}In this example, the use of a structured JSON prompt leads to a clear and concise output that is easy to parse and evaluate. By defining fields such as “summary”, “action_items”, and “priority”, the LLM response becomes more consistent and actionable. Instead of generating free-flowing text, which might vary in style and detail, the model provides a predictable structure that eliminates ambiguity. This approach not only improves the readability and reliability of responses but also makes it easier to integrate the output into downstream workflows, such as project trackers, dashboards, or automated email handlers.
User can control the output
When you frame your prompt in JSON, you remove ambiguity from both the instruction and the output. In this example, asking for a market summary, sentiment, opportunities, risks, and a confidence score can yield inconsistent formats when passed as plain text. However, by structuring the request in JSON — with clearly defined fields like “summary”, “sentiment”, “opportunities”, “risks”, and “confidence_score” — the response becomes predictable, machine-friendly, and easier to parse. This consistency ensures that, whether you’re generating content, analyzing reports, or extracting insights, your workflow remains streamlined and reliable, with no surprises — just clean, structured results every time. Check out the FULL CODES here.
Free-Form Prompt
plain_text_prompt = """
Analyze the following market update:
Market Text:
Tesla's Q2 earnings beat expectations due to higher Model Y sales, but rising competition from BYD is a risk.
Apple reported steady revenue growth driven by iPhone sales, but services revenue slightly declined.
Amazon's AWS division continues to dominate cloud computing, though regulatory scrutiny in Europe is increasing.
Generate:
- A 2-line market summary
- Sentiment for each company (positive, negative, neutral)
- Key growth opportunities and risks
- A confidence score from 0 to 10
"""
response_plain = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-5",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": plain_text_prompt}]
)
plain_output = response_plain.choices[0].message.content
print(plain_output)Market summary:
- Earnings updates skew constructive: Tesla beat on Q2 with strong Model Y, Apple grew on iPhone, and AWS remains the cloud leader.
- Offsetting risks include BYD pressure on Tesla, Apple's services dip, and rising European scrutiny on Amazon.
Sentiment:
- Tesla: Positive
- Apple: Neutral
- Amazon: Positive
Key growth opportunities and risks:
- Tesla
- Opportunities: Sustain Model Y momentum; scale production and pricing to drive volume.
- Risks: Intensifying competition from BYD could pressure share and margins.
- Apple
- Opportunities: Monetize large iPhone base; re-accelerate services via bundles and ecosystem engagement.
- Risks: Services softness; dependence on iPhone for top-line growth.
- Amazon (AWS)
- Opportunities: Leverage leadership to win more enterprise/AI workloads and multi-year commitments.
- Risks: European regulatory scrutiny may lead to fines, compliance costs, or contract/pricing constraints.
Confidence score: 7/10JSON Prompt
json_prompt = """
Analyze the following market update and return the response in this JSON format:
{
"summary": "2-line market overview",
"companies": [
{
"name": "string",
"sentiment": "positive | negative | neutral",
"opportunities": ["list of opportunities"],
"risks": ["list of risks"]
}
],
"confidence_score": "integer (0-10)"
}
Market Text:
Tesla's Q2 earnings beat expectations due to higher Model Y sales, but rising competition from BYD is a risk.
Apple reported steady revenue growth driven by iPhone sales, but services revenue slightly declined.
Amazon's AWS division continues to dominate cloud computing, though regulatory scrutiny in Europe is increasing.
"""
response_json = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-5",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a precise assistant that always outputs valid JSON."},
{"role": "user", "content": json_prompt}
]
)
json_output = response_json.choices[0].message.content
print(json_output)
{
"summary": "Markets saw mixed corporate updates: Tesla beat expectations on strong Model Y sales and AWS maintained cloud leadership.\nHowever, Apple's growth was tempered by softer services revenue while Tesla and AWS face competition and regulatory risks.",
"companies": [
{
"name": "Tesla",
"sentiment": "positive",
"opportunities": [
"Leverage strong Model Y demand to drive revenue and scale production",
"Sustain earnings momentum from better-than-expected Q2 results"
],
"risks": [
"Intensifying competition from BYD",
"Potential price pressure impacting margins"
]
},
{
"name": "Apple",
"sentiment": "neutral",
"opportunities": [
"Build on steady iPhone-driven revenue growth",
"Revitalize Services to reaccelerate growth"
],
"risks": [
"Slight decline in services revenue",
"Reliance on iPhone as the primary growth driver"
]
},
{
"name": "Amazon (AWS)",
"sentiment": "positive",
"opportunities": [
"Capitalize on cloud leadership to win new enterprise workloads",
"Expand higher-margin managed services and deepen customer spend"
],
"risks": [
"Increasing regulatory scrutiny in Europe",
"Potential compliance costs or operational restrictions"
]
}
],
"confidence_score": 8
}
The free-form prompt produced a useful summary but lacked structure, giving the model too much freedom and making it harder to parse programmatically or integrate into workflows.
In contrast, the JSON-prompted result gave the user full control over the output format, ensuring clean, machine-readable results with distinct fields for summary, sentiment, opportunities, risks, and confidence score. This structured approach not only simplifies downstream processing — for dashboards, automated alerts, or data pipelines — but also guarantees consistency across responses. By defining the fields upfront, users effectively guide the model to deliver exactly what they need, reducing ambiguity and improving reliability. Check out the FULL CODES here.
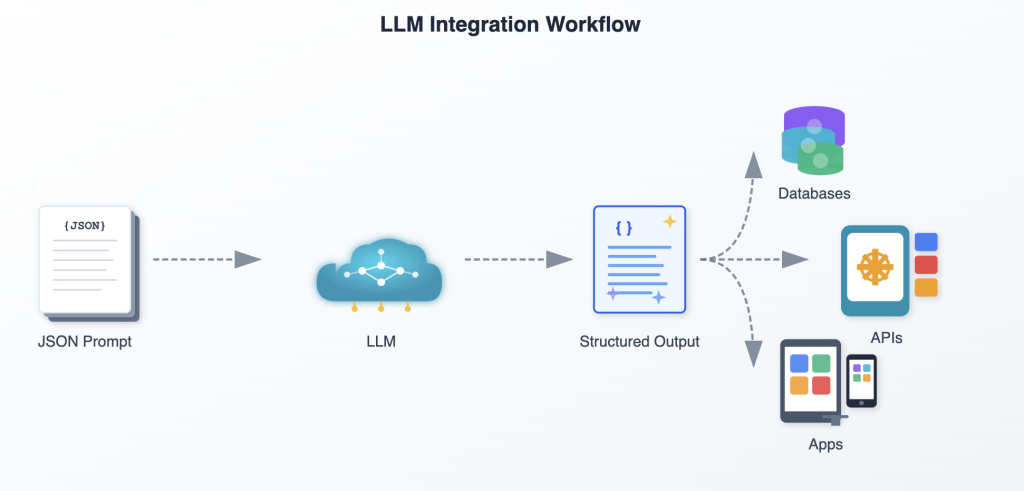
Reusable JSON prompt templates unlock scalability, speed, and clean handoffs.
By defining structured fields upfront, teams can generate consistent, machine-readable outputs that plug directly into APIs, databases, or apps without manual formatting. This standardization not only accelerates workflows but also ensures reliable, repeatable results, making collaboration and automation seamless across projects.

Check out the FULL CODES here and Notes. Feel free to check out our GitHub Page for Tutorials, Codes and Notebooks. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter.
















Leave a comment